24 April 2024 14:48
Education
Safety Delta Netherlands - Academy
Find, connect, renew in safety
Waarom educatie?
Leer meer om je veiligheidssysteem te versterken en verbeteringen te implementerenmet met de InfoNotes of e-learning modules uit de Educatie.
In de Academy, die toegang geeft tot diverse Kenniscollecties over veiligheidsonderwerpen, kun je je blijven ontwikkelen op belangrijke veiligheidsthema’s. Je vindt hier kennis over het bepalen en beheersen van veiligheidsrisico’s, krijgt inzicht in hoe goed beheersmaategelen werken door te meten en te leren van incidenten, en hoe dit ondersteund wordt door een gezonde veiligheidscultuur.
Thema 1: Risicobeheersing en Borging
Determining safety risks, measures to mitigate them and ways to assess that these measures work strongly determine safety performance.
What situations are we talking about?
An incident, or escalation from a minor untoward incident to a major incident, resulting from inadequate mapping of safety risks or not having adequate risk management measures in place.
Interne en/of externe toezichthouders monitoren de staat van de beheersing van de veiligheidsrisico’s. Typische activiteiten zijn:
Setting the business goals to be achieved.
Keeping an overview of relevant laws and regulations, of necessary and obtained permits, and of requirements and wishes of other stakeholders.
Consciously choosing a risk attitude, appetite and tolerance.
Identifying (process) security risks and implementing measures to secure the risks at the chosen maturity level.
Monitor the effectiveness of these measures with an agreed measurement methodology and accurate, complete and timely reports.
Independent evaluation of the safety management system, and its completeness and accuracy, using the reports and improving this system where necessary.
Maintaining knowledge of relevant standards and their changes.
Meer leren
What situations are we talking about?
A cyber security incident resulting in data theft or prolonged asset downtime with consequent financial and reputational costs due to
- a phishing attack in which the attacker attempts to collect information from a user
- a Ransomeware attack, where malicious software is placed at companies to encrypt data that is only released after payment has been made
- an Advanced Persistent Threat attack, where an unauthorised person gains undetected and prolonged access to a network to steal data
- a DDoS attack, in which botnets try to take down companies' servers and prevent users from accessing them
- a Supply Chain Attack, where malware embeds itself in a software package at a software distribution site to steal or manipulate data
Typische maatregelen zijn:
- Install updates
- Control who has access to your data and services
- Check which devices and services are accessible from the Internet and protect them
- Apply multi-factor authentication
- Segment networks
- Back up and test your systems regularly
- Ensure that each application and system generates sufficient log information
- Back up and test your systems regularly
- Encrypt storage media with sensitive business information
- Have a recovery plan and practise it regularly
What situations are we talking about?
An incident resulting from insufficient measures to control emerging risks due to climate change.
Typische maatregelen zijn:
Mapping scenarios with probability and impact due to flooding, peak rainfall, heat or extreme drought.
What situations are we talking about?
Een incident als gevolg van onvoldoende maatregelen voor de beheersing van nieuwe risico’s als gevolg van de energietransitie.
Het in kaart brengen van risico scenario’s en proportionele beheersmaatregelen als gevolg van het toepassen van nieuwe energiedragers.
Thema 2: Veiligheidscultuur en Leiderschap
Safety culture and associated leadership are strong determinants of safety performance.
What situations are we talking about?
An incident, or escalation from a small unusual occurrence to a major incident, resulting from an immature safety culture of an organisation.
In het algemeen hangen de veiligheidsprestaties van een organisatie nauw samen met het niveau van volwassenheid van hun veiligheidscultuur. Typische aspecten zijn:
The tone of the summit
The perception that stakeholders have about what is said about security and what actually happens
The formal and informal decision model of an organisation
The freedom that employees feel to discuss safety topics and the way in which this is subsequently handled
A 'proactive' attitude in dealing with security issues
Setting priorities with regard to safety
The timely and adequate follow-up of improvement actions
Incentives through an organisation's reward system
The learning capacity of an organisation
Competence (knowledge and experience) of employees and managers
What situations are we talking about?
An unusual occurrence that results in environmental nuisance, resulting in financial or reputational damage due to inadequate preparation by neighbours.
Environmental nuisance can include noise, light (flare), odour in situations that are different from 'normal', and the effects of incidents (fire, smoke, pressure wave, impact of fragments, release of (toxic) substances).
Every year in the Netherlands, almost 2000 unusual events are reported and registered by the Human Environment and Transport Inspectorate (ILT). The majority of the unusual occurrences in 2020 concerned small leaks or emissions to air, soil or surface water (56%), flaring (13%), (un)planned installation stops or maintenance (10%) and fire (7%).
Typische aspecten van veiligheidsbeleving zijn:
Focus communication efforts on people who live or work near the chemical cluster / Brzo companies.
Provide prompt, honest and transparent information during events that are perceived as incidents. This can also be maintenance.
Provide more openness and transparency in what parties are doing to increase safety, how this is being monitored, how lessons have been learned from the past, and how parties are taking the interests and concerns of local residents into account.
Promote information explicitly through multiple channels and make clear how your company and/or the regulator can be reached in case of questions.
What situations are we talking about?
An incident, or escalation from a minor unusual occurrence to a major incident, resulting from insufficient competence and/or capacity to identify and control safety risks.
Typische beheersmaatregelen zijn:
Establish competence requirements for activities that are safety-critical.
Use standard operating procedures.
Emphasise on-the-job training.
Thema 3: Meten van Veiligheidsprestaties en Leren van Incidenten
Measuring is knowing, and learning is the basis for improving safety.
What situations are we talking about?
An incident, or escalation from a small unusual occurrence to a major incident, because one or more parts of the safety management system are found not to be working properly.
Site-specific indicators, aimed at tracking the state of the safety management system over time, help to keep the system of measures to control safety risks in order.
These are often combinations of leading and lagging indicators. Leading indicators are often designed to provide information about the state of work processes. Lagging indicators are usually outcomes.
Implementation of indicators includes:
Choose a limited number of leading indicators for the most important work processes and make sure they are meaningful and usable for the employees who carry out these processes.
Regularly collect the results from parts of the organisation (or sector) and aggregate the results.
Use leading and lagging indicators in management reviews to assess the state of the measures taken and initiate improvements where necessary.
Use industry standards for the definition of lagging indicators.
Use lagging indicators to compare the performance of organisations with the aim of learning from others.
Meer leren
What situations are we talking about?
An incident, or escalation from a small unusual occurrence to a major incident, resulting from inadequate learning from incidents and near misses in one's own organisation or those of others.
Typische beheersmaatregelen zijn:
Promoting a safety culture in which all incidents or unusual occurrences are reported to managers.
The timely and systematic gathering of information about the incident (what, when, who) where the depth of information gathering depends on the consequences of the incident.
Reporting of incidents to the competent authority in a timely and complete manner.
Conducting thorough incident investigations of cases with the highest learning potential (why).
Having a learning session with the organisation's management team and prioritising possible improvements in existing measures to ensure (process) safety.
Monitor timely and complete follow-up of these identified actions.
Sharing lessons within the organisation, with the competent authority and with the sector.
Assessing lessons learned from others for possible improvements to one's own measures to ensure (process) safety.
Meer leren
Thema 4: Procesveiligheid en Asset Integrity Management
Process Safety Management and the associated Asset Integrity Management are strong determinants of safety performance.
What situations are we talking about?
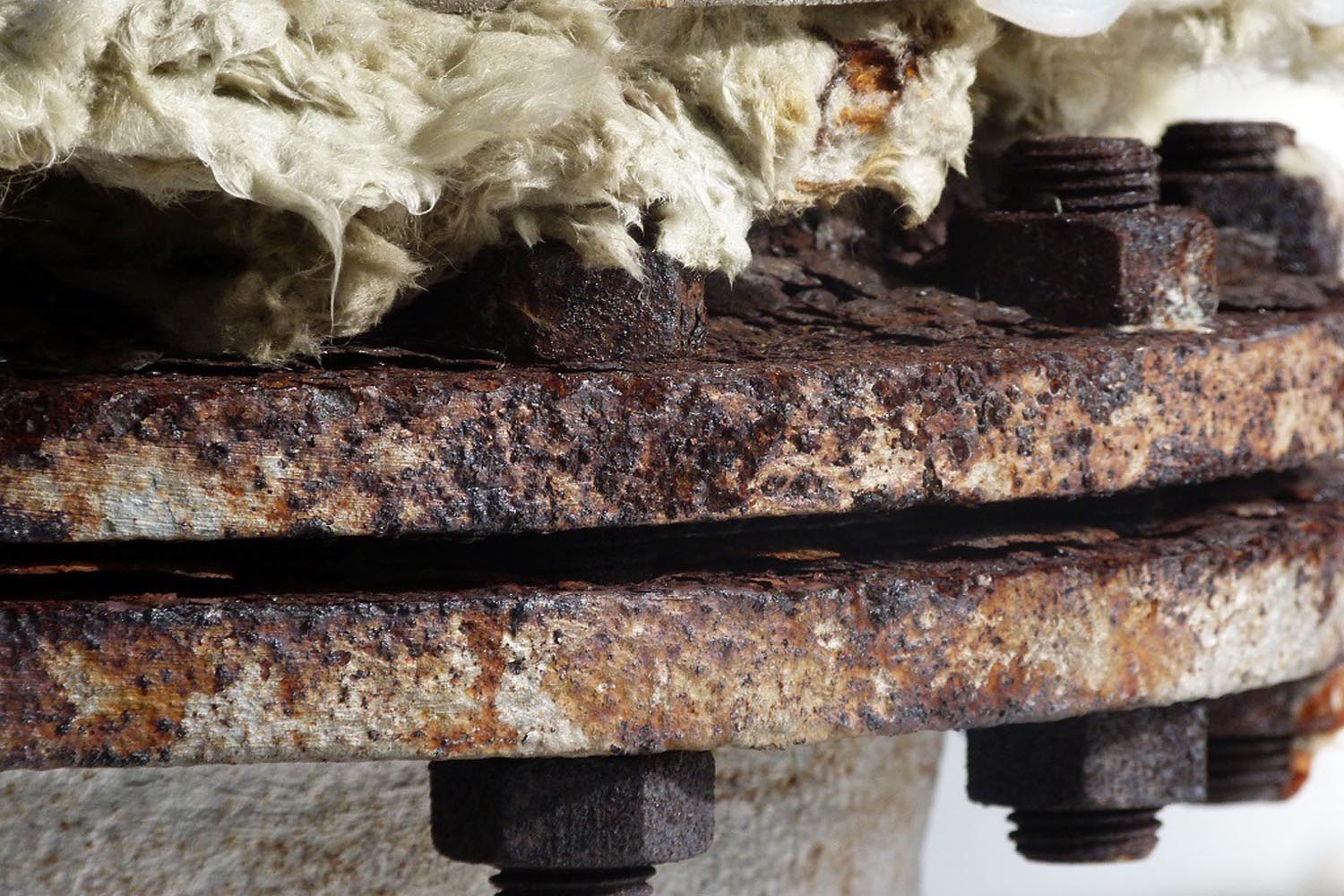
Prevention of an incident, or escalation from a minor unusual occurrence to a major incident, due to corrosion under insulation at facilities where hazardous materials are used.
Mapping parts of an installation at high risk of corrosion under insulation
Regular inspection of these areas, including the condition of the applied insulation material
Application of coatings